Understanding Danger Elements, Not Causation
Find out how a lot Tylenol pregnant ladies can safely take, what threat elements matter, and why glutathione standing—not acetaminophen itself—determines security throughout being pregnant.
IN THIS ARTICLE
• Key Takeaways: Tylenol Security for Pregnant Ladies
• Tylenol for Pregnant Ladies: What You Have to Know
• The Timeline: Tylenol Introduction and Rising Neurodevelopmental Dysfunction Charges
• Why Glutathione Issues for Mind Growth
• What the Analysis Exhibits About Tylenol and Being pregnant
• How A lot Tylenol Can I Take Whereas Pregnant? Present Utilization Patterns
• How Tylenol Is Metabolized: The Three Pathways
• How Being pregnant Modifications Acetaminophen Metabolism
• What Slows and Speeds Up Your Detox Enzymes
• The Toxicity of NAPQI: Why This Metabolite Is Harmful
• Who Could Be at Greater Danger? Your Particular person Security Profile
• The Postnatal Danger: Tylenol After Vaccination
• The Backside Line: Is Tylenol Protected for Being pregnant?
• Steadily Requested Questions
• Full References
KEY TAKEAWAYS: TYLENOL SAFETY FOR PREGNANT WOMEN
• Tylenol itself isn’t poisonous—it solely turns into problematic when your physique can not correctly metabolize it via secure cleansing pathways
• The important thing issue is glutathione standing: Glutathione acts as your physique’s grasp antioxidant and is important for each safely processing acetaminophen and supporting wholesome fetal mind growth[¹⁻²⁻³⁻⁴⁻⁵]†
• Excessive-risk situations: PCOS (50% decrease glutathione[¹⁷⁻³⁷⁻⁴⁰]), IVF conception (70-83% depleted antioxidants[¹⁸⁻¹⁹⁻⁴¹⁻⁴⁶]), gestational blood sugar regulation points, gallbladder dysfunction[⁵³⁻⁶⁰], and choline deficiency (89% of pregnant ladies[⁶¹⁻⁶³])
• 62-65% of pregnant ladies use Tylenol throughout being pregnant, with commonplace doses of 500-650 mg each 4-6 hours[¹⁵⁻¹⁶⁻²⁰]
• Being pregnant metabolism shifts INCREASE toxicity: 80% enhance within the pathway that generates poisonous NAPQI, with 43% MORE NAPQI in first trimester when fetal mind is most susceptible, 33% LESS sulfation capability, and glutathione depleted 36-87% all through being pregnant[⁶⁰⁻¹⁰²⁻¹⁰⁴]
• Analysis exhibits dose-response relationships: Longer acetaminophen use correlates with greater consideration/focus issues and neurodevelopmental dysfunction threat, with kids having highest twine blood metabolites dealing with 2-3x greater odds[¹¹⁻¹⁴⁻⁷⁷⁻⁷⁹]
• The poisonous metabolite NAPQI crosses the placenta and depletes fetal mind glutathione at doses under these inflicting maternal liver toxicity[²⁴⁻²⁵⁻⁷³⁻⁷⁵⁻¹⁰⁰]
• Submit-birth vulnerability continues: Will increase workload on immature cleansing system. Depletion of glutathione impairs neurodevelopment. 64% of infants obtain acetaminophen after vaccination[⁴⁷⁻⁴⁸]
The objective isn’t to create concern—it’s to grasp that particular person metabolic context issues when figuring out how a lot Tylenol is secure for pregnant ladies.
TYLENOL FOR PREGNANT WOMEN: WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
When looking out “is Tylenol secure for being pregnant” or “how a lot Tylenol can I take whereas pregnant,” expectant moms encounter alarming headlines linking prenatal acetaminophen use to neurodevelopmental issues and a spotlight/focus issues. However does Tylenol trigger these situations? The proof suggests one thing extra nuanced—and extra necessary for pregnant ladies to grasp.
The important thing lies in understanding glutathione—glutathione acts as your physique’s grasp antioxidant, important for wholesome fetal mind growth.† Acetaminophen (Tylenol, paracetamol) metabolism straight depletes glutathione.[¹⁻⁵] The essential query is: what occurs when ladies who have already got low glutathione standing take Tylenol in the course of the essential window of fetal mind growth?
The dramatic enhance in neurodevelopmental dysfunction prevalence—from uncommon to affecting 1 in 36 kids—factors strongly to environmental elements. Tylenol use throughout being pregnant seems to be one piece of this bigger environmental puzzle.[⁹⁰⁻⁹⁹]
THE TIMELINE: TYLENOL INTRODUCTION AND RISING NEURODEVELOPMENTAL DISORDER RATES
The temporal correlation between widespread acetaminophen use and neurodevelopmental dysfunction prevalence is placing:
ACETAMINOPHEN INTRODUCTION AND ADOPTION[⁸³⁻⁸⁹]
• 1955: Tylenol (acetaminophen) launched for medical use in america
• Nineteen Sixties-Seventies: First use in being pregnant for ache and fever administration
• Eighties: Broadly really useful as first-line agent for ache and fever in being pregnant
• Late Eighties-Nineteen Nineties: Elevated use for post-vaccination symptom administration in infants (changing aspirin attributable to Reye’s syndrome issues)
• 2000s-present: Routine use in newborns/infants after vaccination; 62-65% of pregnant ladies use acetaminophen throughout being pregnant
• By 9 months of age: As much as 95% of kids have been uncovered to acetaminophen
NEURODEVELOPMENTAL DISORDER PREVALENCE TIMELINE[⁹⁰⁻⁹⁹]
• Nineteen Sixties: Prevalence estimated at 1 in 10,000
• Eighties: Prevalence rises to 1 in 2,000
• Late Eighties-Nineteen Nineties: Charges start dramatic enhance
• Late Nineteen Nineties: Prevalence reaches 1 in 200
• 1996-2010: 269% enhance in ASD prevalence (Atlanta surveillance information)
• 2021: Prevalence reaches 1 in 44 in america
• 1998-2018: 787% enhance in recorded incidence within the UK
THE TEMPORAL PATTERN
The dramatic rise started within the late Eighties and accelerated via the Nineteen Nineties and 2000s—roughly 25-30 years after acetaminophen’s introduction and widespread adoption in being pregnant, and coinciding with elevated use for post-vaccination symptom administration in infants.
Whereas modifications in diagnostic standards, elevated consciousness, and improved screening clarify a part of this enhance, research counsel that environmental exposures may additionally contribute to a real rise in prevalence. The timing aligns with the interval when acetaminophen turned ubiquitous in being pregnant and early childhood—affecting each prenatal mind growth and postnatal exposures throughout essential developmental home windows.
This temporal correlation doesn’t show causation, but it surely helps the speculation that acetaminophen could also be considered one of a number of environmental elements contributing to rising neurodevelopmental dysfunction charges, notably in metabolically susceptible populations unable to securely detoxify the drug.
WHY GLUTATHIONE MATTERS FOR BRAIN DEVELOPMENT†
Glutathione acts as your physique’s grasp antioxidant and first mechanism for supporting growing tissue’s wholesome response to oxidative stress. Throughout being pregnant, sufficient glutathione ranges are important for correct mind growth.[¹⁻⁵]†
GLUTATHIONE’S CRITICAL ROLES[¹⁻⁵]†
• Helps the growing mind’s wholesome response to oxidative stress
• Helps wholesome methylation (controls gene expression)
• Regulates homocysteine ranges (elevated ranges threat neural tube defects)
• Allows correct epigenetic programming
• Helps a wholesome immune response inside the mind and spinal chord and regular microglial activation
THE CONNECTION TO NEURODEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS
Youngsters with neurodevelopmental issues persistently present low glutathione ranges, elevated homocysteine, impaired methylation capability, oxidative stress markers, and mitochondrial dysfunction.[⁶⁻⁸]
Low maternal glutathione throughout being pregnant is related to preeclampsia, HELLP syndrome, intrauterine development restriction, fetal mind irritation, and neurodevelopmental issues.[²⁻³⁻⁶⁻⁹⁻¹⁰]
WHAT THE RESEARCH SHOWS ABOUT TYLENOL AND PREGNANCY
A number of giant observational research establish associations between prenatal acetaminophen use and neurodevelopmental outcomes:
• A 2021 meta-analysis of 73,881 mother-child pairs discovered kids prenatally uncovered to acetaminophen had been 19% extra prone to have signs related to neurodevelopmental situations and 21% extra prone to have consideration/focus signs.[¹¹]
• A 2020 examine measuring twine blood biomarkers discovered dose-response relationships with consideration/focus issues and neurological issues threat.[¹²]
• A 2018 meta-analysis of 132,738 mother-child pairs discovered associations that elevated with longer publicity period.[¹³]
• A 2024 analysis reviewed 46 research, with higher-quality research extra prone to present optimistic associations.[¹⁴]
HOW MUCH TYLENOL CAN I TAKE WHILE PREGNANT? CURRENT USAGE PATTERNS
• 62-65% of pregnant ladies use acetaminophen at the very least as soon as[¹⁵⁻¹⁶]
• 6% use it weekly or extra typically[¹⁵⁻¹⁶]
• Customary dose: 500-650 mg each 4-6 hours as wanted[¹⁵⁻¹⁶⁻²⁰]
• 58% use it for fewer than 10 days; 9% use it for 45+ days[¹⁶]
These “secure” therapeutic doses can considerably deplete glutathione in ladies who have already got low baseline ranges.[²¹⁻²³] Wholesome people can tolerate as much as 4g/day with solely modest glutathione lower, however people with compromised glutathione expertise vital depletion even at therapeutic doses.
THE MATH THAT MAKES YOU STOP AND THINK
• Neurodevelopmental dysfunction charge: 1 in 36 kids
• 3.6 million births per 12 months within the USA
• 1:36 = 100,000 kids identified yearly
• 65% of pregnant ladies take acetaminophen (2.3 million ladies yearly)
• At the very least 10% have compromised glutathione (PCOS, IVF, poor food regimen, chemical publicity, genetics)
• That’s 200,000+ pregnancies per 12 months the place acetaminophen depletes the molecule wanted for wholesome mind growth
If even half of these 200,000 susceptible pregnancies end in developmental points, you’ve accounted for a good portion of the affected inhabitants.
HOW TYLENOL IS METABOLIZED: THE THREE PATHWAYS
While you take acetaminophen, your liver processes it via three main pathways:[²⁶⁻²⁷⁻⁶⁰⁻⁷⁰⁻⁷²]
1. GLUCURONIDATION – SAFE PATHWAY (UGT1A6 enzyme)
• 50-60% of acetaminophen in wholesome non-pregnant adults
• Attaches glucuronic acid to make it water-soluble for urinary excretion
• Protected, non-toxic pathway
• INCREASES throughout being pregnant: 6% in first trimester, rising to 19% by third trimester[⁶⁰]
• Severely underdeveloped in fetuses/newborns
2. SULFATION – SAFE PATHWAY (SULT enzymes)
• 30-35% of acetaminophen in wholesome non-pregnant adults
• Attaches sulfate teams for secure elimination
• Non-toxic pathway
• DECREASES 33% throughout being pregnant (opposite to earlier assumptions)[⁶⁰]
• Restricted capability—simply saturated with repeated doses
• Predominant pathway in fetuses/kids (60-70%) however rapidly overwhelmed
3. OXIDATION – TOXIC PATHWAY (CYP2E1 enzyme)
• Solely 5-10% of acetaminophen in wholesome non-pregnant adults
• INCREASES by 80% throughout being pregnant[⁶⁰]
• Creates NAPQI (N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine)—the poisonous metabolite
• NAPQI formation 43% HIGHER in first trimester[⁶⁰]
• NAPQI should be instantly neutralized by glutathione
• When glutathione is depleted, NAPQI causes mobile harm
• Crosses the placenta and damages fetal mind
HOW PREGNANCY CHANGES ACETAMINOPHEN METABOLISM
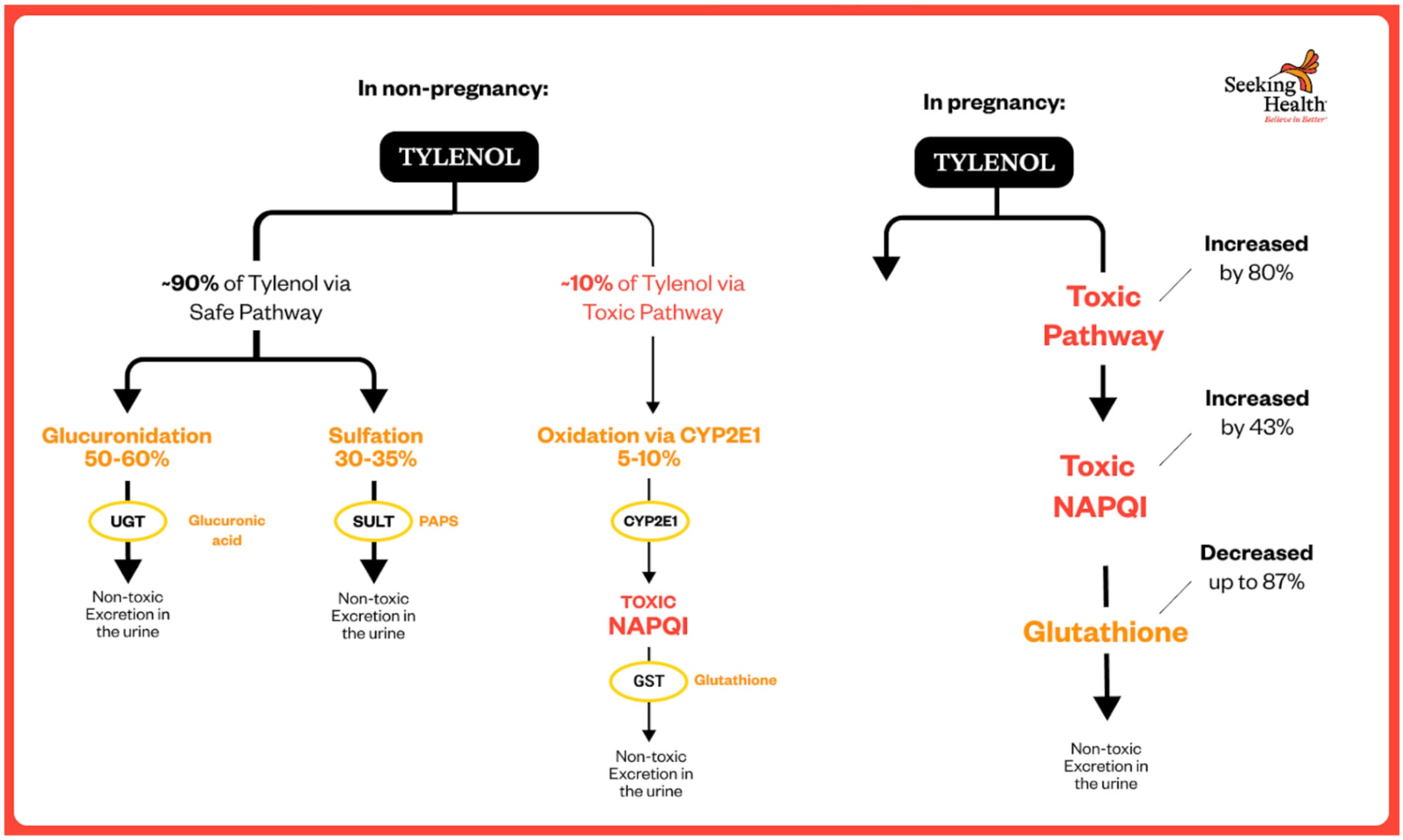
METABOLIC PATHWAY CHANGES DURING PREGNANCY[⁶⁰⁻¹⁰⁰⁻¹⁰¹]
Human pharmacokinetic research reveal dramatic shifts in how pregnant ladies metabolize acetaminophen:
Oxidation to NAPQI (Poisonous Pathway) INCREASES by 80%
The Brookhuis et al. 2021 examine revealed in Pharmaceutics used physiologically-based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) modeling in pregnant ladies and located:
Simply earlier than giving delivery, the clearance stage (CL) of acetaminophen through the poisonous pathway was “1.8-fold greater than shortly after supply. This 80% enhance, noticed in third-trimester pregnant ladies was estimated to happen all through your complete being pregnant.”[⁶⁰]
This implies **43% MORE of the poisonous NAPQI metabolite is produced** throughout being pregnant in comparison with non-pregnant ladies.
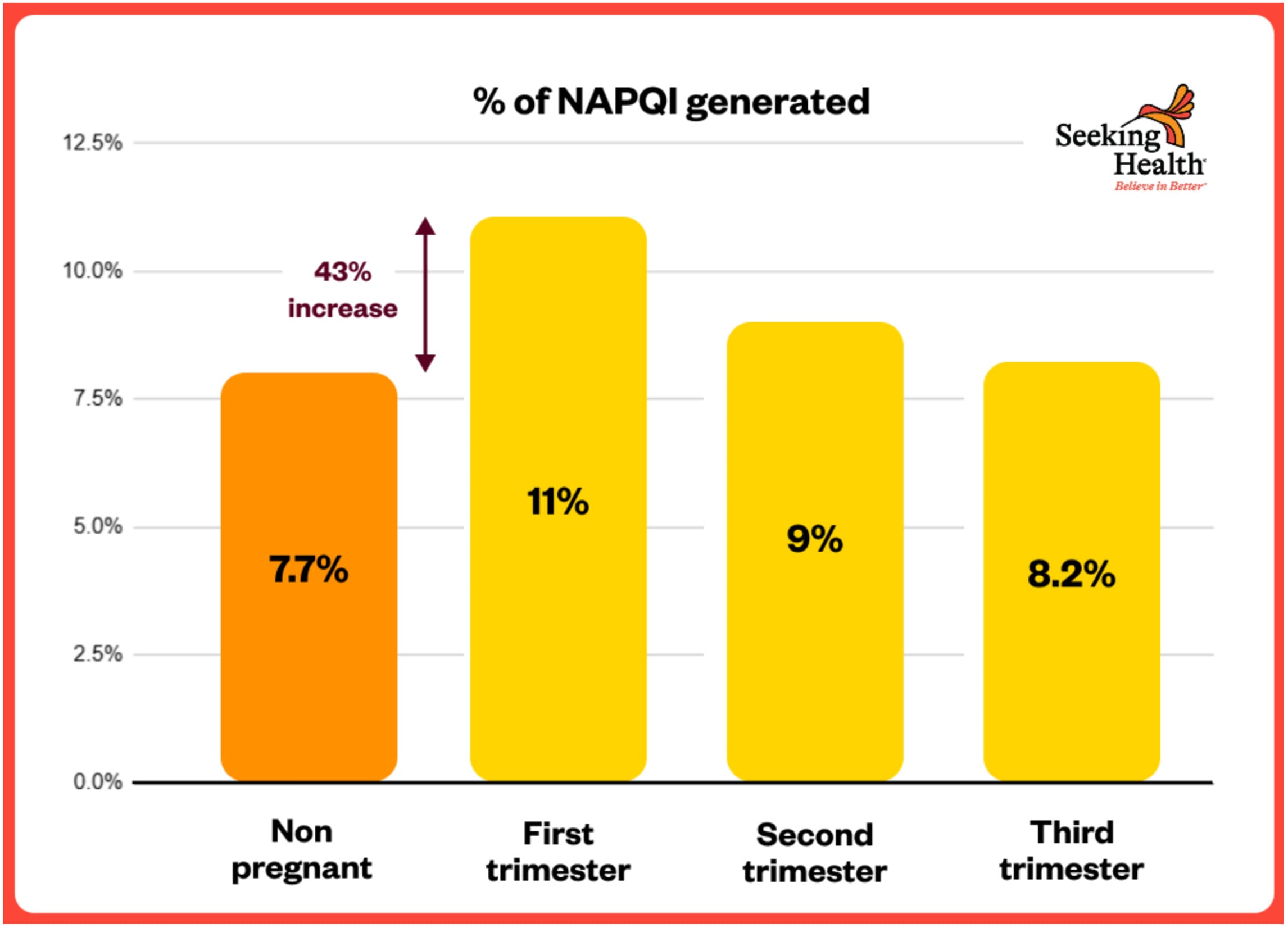
NAPQI Formation Highest in FIRST Trimester – 43% HIGHER
The identical Brookhuis 2021 examine discovered:
“The estimated molar dose fraction of NAPQI was the very best within the first trimester (median (IQR): 11 (9.1–13.4%), adopted by the second (9.0 (7.5–11%)) and third (8.2 (6.8–10.1)) trimester in contrast with non-pregnant ladies (7.7 (6.4–9.4%)).”[⁶⁰]
**This represents a 43% INCREASE in poisonous NAPQI formation within the first trimester** (11% vs 7.7%)—exactly when the fetal mind is most susceptible and present process essential early growth.
Sulfation (Protected Pathway) DECREASES 33%
The Brookhuis 2021 information confirmed:
“The estimated molar dose fraction of acetaminophen-sulphate decreased with the period of being pregnant (24.2 (22.3–26.2%), 21.5 (19.9–23.1%) and 20.7 (19.1–22.4%) within the first, second and third trimester, respectively) in contrast with non-pregnant ladies (31.1 (29.0–33.3%)).”[⁶⁰]
**It is a 33% DECREASE within the secure sulfation pathway by third trimester** (20.7% vs 31.1%).
Glucuronidation Will increase BUT Is Inadequate
Whereas glucuronidation (the opposite secure pathway) does enhance throughout being pregnant:
This enhance in glucuronidation CANNOT compensate for the simultaneous:
• 33% lower in sulfation (one other secure pathway)
• 80% enhance in oxidation to poisonous NAPQI
**The End result:** When each secure pathways grow to be saturated or overwhelmed, considerably extra acetaminophen is compelled via the poisonous CYP2E1 pathway, creating 43% extra NAPQI—at exactly the time when glutathione reserves are most depleted.
GLUTATHIONE DEPLETION DURING PREGNANCY[¹⁰²⁻¹⁰⁵]
A number of human research verify that glutathione ranges progressively DECREASE all through being pregnant—creating most vulnerability when mixed with elevated NAPQI manufacturing.
Progressive Depletion Throughout Trimesters
A 2024 examine measuring glutathione throughout all three trimesters discovered:[¹⁰²]
“The present examine exhibits there was a major distinction in serum glutathione ranges within the first, second and third trimester (sub teams) when in comparison with management group (48.21 ±1.13 pg./ml), (34.01 ±1.02 pg./mL), (9.76 ±0.34 pg./mL) vs. (75.24 ±1.29 pg./mL), (P≤0.01).”
This represents:
• **36% LOWER glutathione in first trimester** (48 vs 75 pg/mL)
• **55% LOWER in second trimester** (34 vs 75 pg/mL)
• **87% LOWER in third trimester** (9.76 vs 75 pg/mL)
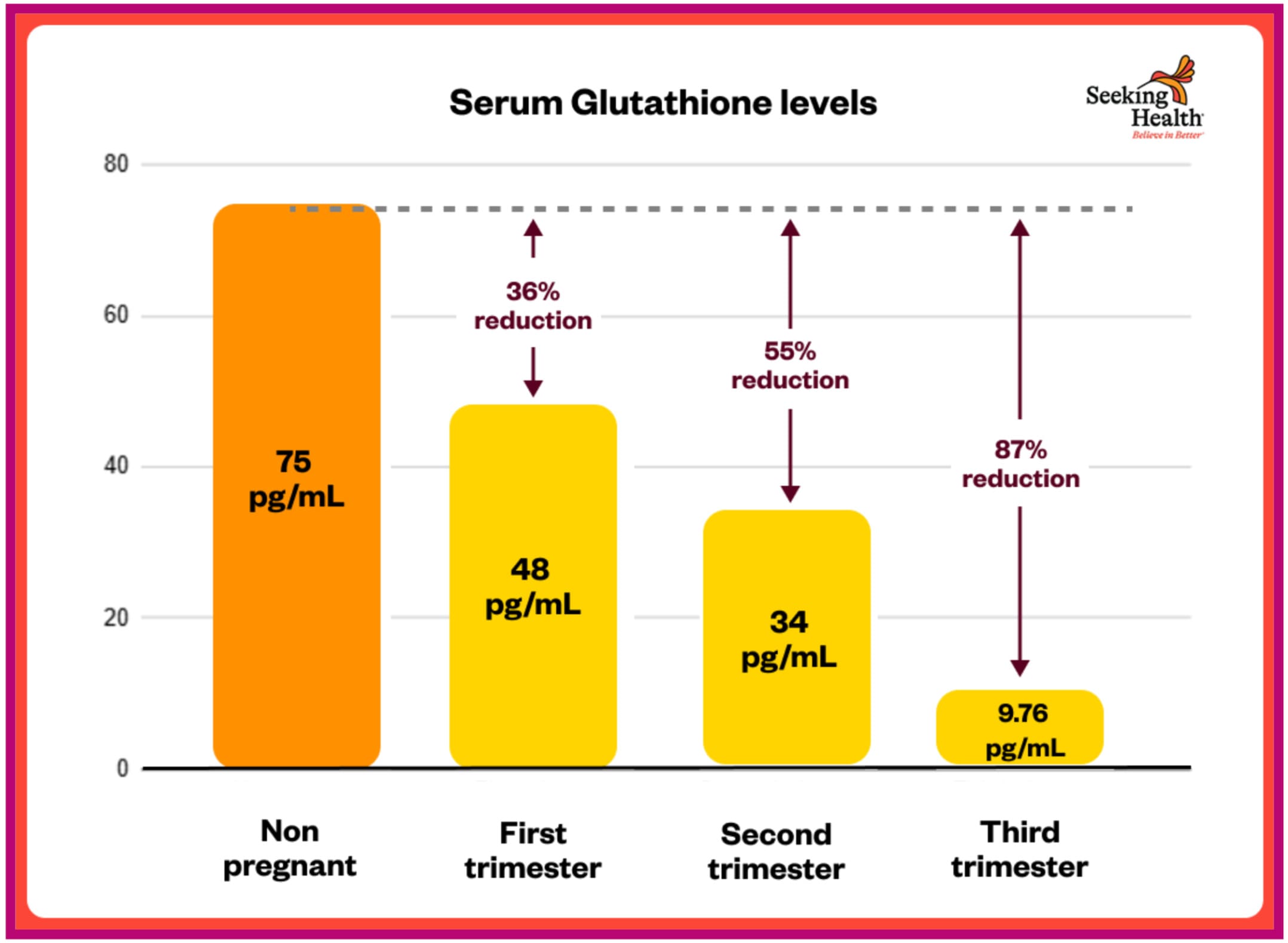
The examine concluded: “The lower in antioxidant ranges and enhance in malondialdehyde (MDA) stage [an indicator of oxidative stress] lead us to conclude that being pregnant as a state of affairs produces an enormous quantity of oxidant so reduces the potential of the physique to beat its impact resulting in oxidative stress.”[¹⁰²]
>>> Glutathione Depletion in Regular Being pregnant <<<
A separate examine confirmed: “It was discovered that the glutathione ranges in second trimester of being pregnant had been discovered to be lower than non-pregnant ladies” and “Serum glutathione ranges are considerably decrease in pregnant ladies than non-pregnant ladies. (p <0.0001).”[¹⁰³]
Additional Depletion in Being pregnant Issues
Kharb 2000 discovered: “In preeclampsia, maternal whole glutathione ranges had been decrease than in regular being pregnant (P<0.001). Additionally, diabetic preeclamptics confirmed low whole glutathione ranges as in comparison with preeclampsia (P<0.05) and management (P<0.001). These findings point out decreased detoxificating or free radical scavenging capability in pregnancies sophisticated by preeclampsia and diabetes.”[¹⁰⁴]
THE PERFECT STORM: PREGNANCY CREATES MAXIMUM VULNERABILITY
The mix of those metabolic modifications creates unprecedented threat:
1. **↑ 80% INCREASE within the poisonous NAPQI pathway** (43% extra NAPQI generated in first trimester)
2. **↓ 33% LESS sulfation capability** (secure detox pathway decreases)?
3. **↓ 36-87% LOWER glutathione** (wanted to neutralize NAPQI)
4. **Fetal mind extremely susceptible** (immature detox enzymes, excessive metabolic calls for)
Because of this therapeutic doses thought-about “secure” in non-pregnant ladies may be poisonous throughout being pregnant—particularly in metabolically susceptible populations with already-compromised glutathione standing.
THE TOXICITY OF NAPQI: WHY THIS METABOLITE IS DANGEROUS
Acetaminophen itself isn’t poisonous. It solely turns into poisonous when metabolized into NAPQI. The issue arises throughout being pregnant when the poisonous oxidation pathway will increase by 80%, producing 43% extra NAPQI within the first trimester—at exactly the time when glutathione is depleted 36-87%.[⁶⁰⁻¹⁰²⁻¹⁰⁴]
NAPQI CROSSES THE PLACENTA AND DAMAGES THE FETUS[²⁴⁻²⁵⁻¹⁰⁰]
The Mian et al. 2020 examine confirmed:[¹⁰⁰]
• NAPQI crosses the placenta
• Fetal liver has severely restricted cleansing capability
• Demonstrates direct fetal publicity to poisonous metabolite
WHAT NAPQI DOES[⁷³⁻⁷⁵]
• Immediately binds to and damages mobile proteins
• Depletes glutathione quickly
• Generates oxidative stress which damages lipids, proteins, and DNA
• Triggers cell dying (apoptosis)
• Damages mitochondria, disrupting power manufacturing
NAPQI DEPLETES FETAL BRAIN GLUTATHIONE AT DOSES BELOW MATERNAL LIVER TOXICITY
ESSENTIAL POINT: NAPQI depletes fetal mind glutathione and induces oxidative stress and cell dying in neural tissue at doses under these inflicting maternal liver toxicity.[⁷⁵] The growing mind has restricted antioxidant defenses and excessive metabolic calls for, making it particularly inclined.
Because of this a pregnant girl can really feel superb whereas her fetus is experiencing glutathione depletion and oxidative mind harm.
WHY LOW GLUTATHIONE IS DEVASTATING FOR THE DEVELOPING BRAIN
When NAPQI binds to glutathione, it reduces capability for glutathione to detoxify different dangerous chemical compounds within the growing mind, akin to:
#1 Hydrogen Peroxide
Glutathione usually converts hydrogen peroxide into water. Within the growing mind, hydrogen peroxide:
• Kills immature neurons at concentrations much less poisonous to mature neurons
• Disrupts the blood-brain barrier
• Impairs visible system growth and mind connectivity
#2 Formaldehyde
Naturally produced within the physique however elevated by environmental publicity (new garments, carpets, building supplies). Within the growing mind, formaldehyde:
• Disrupts studying and reminiscence
• Causes oxidative stress and DNA harm
• Promotes irritation and cell dying
• Disrupts neurotransmitter methods
#3 Poisonous Metals
Mercury and arsenic are well-established neurotoxicants. Within the growing mind:
• Mercury (methylmercury from fish) causes dose-dependent deficits in IQ, reminiscence, consideration, language
• Arsenic publicity (rice, ingesting water) linked to cognitive deficits, decrease IQ, behavioral points
• First trimester is especially susceptible
#4 Homocysteine
Maternal homocysteine will increase with inadequate folate and vitamin B12. Excessive homocysteine throughout being pregnant is related to:
• Neural tube defects
• Delayed mind maturation
• Cognitive deficits
WHY THE DEVELOPING BRAIN IS MORE VULNERABLE
• Greater metabolic exercise: Speedy development generates extra reactive oxygen species
• Decrease protecting enzymes: Much less capability to detoxify hydrogen peroxide
• Immature blood-brain barrier: Extra permeable to chemical compounds and toxins
• Underdeveloped myelin: Neurons lack fatty protecting coating (not totally developed till at the very least age 3)
• Underdeveloped cleansing: Fetal and new child liver capability severely restricted
THE LINK TO NEURODEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS
Consideration/Focus Problems – Most Strong Proof[⁷⁷⁻⁷⁹]
• Clear dose-response relationship: extra publicity = greater threat
• Wire blood biomarkers of NAPQI cleansing: 2–3-fold greater odds of ADHD
Neurodevelopmental Spectrum Problems[⁷⁷⁻⁷⁹⁻⁸¹]
• Much less constant than Consideration/Focus issues
• Greater twine plasma metabolite ranges related to elevated odds in some cohorts
• Greater-quality research extra prone to present optimistic associations
Different Outcomes[⁸¹⁻⁸²]
• Sleep and behavioral issues in uncovered toddlers
• Slight enhance in mental incapacity threat
**THE DOSE-RESPONSE PATTERN[⁷⁷⁻⁷⁹]**
• Brief-term use (<1 week): Minimal to modest threat enhance
• Longer period (a number of weeks): Progressively greater threat
• Frequent use (weekly+): Highest threat
• Greater twine blood metabolites: 2-3x greater odds of consideration & focus/neurodevelopmental issues
That is precisely what you’d anticipate if NAPQI is the motive force: extra acetaminophen → extra NAPQI → extra glutathione depletion → extra oxidative harm → greater neurodevelopmental threat.
RISK FACTORS FOR TYLENOL DURING PREGNANCY
DIETARY RISK FACTORS
• **Low sulfur amino acid consumption** – Vegetarian/vegan diets with out sufficient protein, low eggs/poultry/fish/cruciferous greens
• **Protein-energy malnutrition** – Inadequate energy, fasting, insufficient protein
• **Micronutrient deficiencies** – Low nutritional vitamins C and E (impair glutathione recycling), selenium, B nutritional vitamins (B6, B12, folate)
METABOLIC AND HEALTH CONDITIONS
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) – Main Concern (5-10% of girls)[¹⁷⁻³⁷⁻⁴⁰]
• 50% decrease glutathione ranges
• Considerably elevated oxidative stress
• 3-4x greater threat of preeclampsia, 3x greater threat of gestational diabetes—each additional deplete glutathione
• Crucial dose concern: With 50% decrease baseline glutathione, the “secure” dose is successfully lower in half
Different metabolic situations that cut back glutathione standing:
• Blood sugar dysregulation – Gestational blood sugar points, pre-existing blood sugar points, high-sugar food regimen
• Power infections – Viral (EBV, CMV), bacterial, persistent inflammatory situations
• Pre-existing liver situations – Fatty liver, persistent hepatitis
• Weight problems and metabolic syndrome – Power irritation, impaired glutathione synthesis
ENVIRONMENTAL EXPOSURES
• **Chlorine** – Faucet water, swimming pools, scorching tubs
• **Formaldehyde and VOCs** – New clothes (unwashed), new carpets/flooring, transformed houses, new furnishings, nail salons, hair salons
• **Different chemical compounds** – Pesticides, heavy metals, air air pollution, occupational exposures, cleansing merchandise
LIFESTYLE FACTORS
• **Excessive-intensity train** – Exhaustive train can acutely deplete glutathione
• **Power stress and insufficient sleep** – Will increase oxidative stress, depletes glutathione
GENETIC FACTORS
Variants in CBS, CYP2E1, glutathione pathway genes, MTHFR, GSTM1/GSTT1 deletions, UGT enzyme polymorphisms
MEDICATION AND SUBSTANCE USE
Power alcohol, CYP2E1-inducing medicine, medicines burdening glutathione methods, a number of medicines competing for glucuronidation, estrogen-containing contraceptives (prior use), fertility drug use
PREGNANCY-SPECIFIC FACTORS
Gallbladder Dysfunction (10% of pregnant ladies)[⁵³⁻⁶⁰⁻¹⁰⁶⁻¹⁰⁷]
• As much as 10% develop gallstones or biliary sludge
• Intrahepatic cholestasis of being pregnant (ICP): 0.4-10% of pregnancies (as much as 5.6% in Latina ladies)
• Sluggish gallbladder operate impairs hepatic clearance
!!! CRITICAL: FATAL OUTCOMES DOCUMENTED AT THERAPEUTIC DOSES !!!
Gao et al. 2022 reported the primary case of a pregnant girl with intrahepatic cholestasis who died from liver failure after taking THERAPEUTIC/NORMAL doses of acetaminophen: “Hepatic Failure With Deadly Final result Throughout Being pregnant Following Administration of a Single Therapeutic Dose of Acetominophen.”[⁵⁸]
This case represents the FIRST documented deadly end result from therapeutic-dose acetaminophen in being pregnant, demonstrating that commonplace doses may be deadly in metabolically susceptible pregnant ladies.
Liver Transplants Required at Supratherapeutic Doses
Thornton & Minns 2012 documented:[¹⁰⁶]
• 22-year-old pregnant girl
• Took 8-9 grams/day for 10-14 days (vs 4g/day most really useful)
• Developed fulminant hepatic failure requiring liver transplant
• Fetal demise occurred 2 weeks post-transplant
A second liver transplant case (2013):
• 22-year-old, 19 weeks pregnant
• Took roughly 6 grams day by day for two weeks for toothache
• Developed fulminant hepatic failure requiring transplantation
• Fetus expired
These instances display that doses reasonably above really useful limits—which is perhaps tolerated in non-pregnant ladies—may cause catastrophic liver failure requiring transplantation throughout being pregnant, with fetal dying as a standard end result.
Choline Deficiency (89% of pregnant ladies)[⁶¹⁻⁶³]
• Solely 11% of pregnant ladies meet really useful choline consumption
• Even worse for vegetarian/vegan diets (solely 7% sufficient)
• Choline important for liver operate, methylation, and phospholipid synthesis
• Deficiency will increase susceptibility to hepatic damage
IVF/Assisted Reproductive Expertise (2-5% of births)[¹⁸⁻¹⁹⁻⁴¹⁻⁴⁶]
Ladies who conceive through IVF expertise dramatic antioxidant depletion:
• 70% discount in plasma antioxidant capability (3.4-fold decrease than pure conception)
• 83% discount in follicular fluid antioxidant capability (6-fold decrease)
• 10-30% lower in whole antioxidant exercise after ovarian stimulation
• 15-25% lower in nutritional vitamins E, C, carotenoids throughout IVF cycle
• 50-100%+ enhance in oxidative stress markers
• Decrease essential hint parts (copper, iron, zinc, magnesium)
• Diminished glutathione S-transferase exercise in follicular fluid
Crucial dose concern: With 70-83% lowered antioxidant capability, even a single 500 mg dose represents a a lot better burden. With over 5 million infants born through IVF globally (half in previous 6 years), this represents a big and rising high-risk inhabitants.
**Different pregnancy-specific threat elements:** Preeclampsia, gestational blood sugar points, gestational hypertension, a number of gestations, hyperemesis gravidarum, superior maternal age, historical past of being pregnant problems
THE POSTNATAL RISK: TYLENOL AFTER VACCINATION
If prenatal acetaminophen creates vulnerability throughout fetal mind growth, post-vaccination acetaminophen in infants might symbolize the ultimate burden on an already compromised system.
HOW COMMON IS POST-VACCINATION TYLENOL USE?
• 64% of infants obtain acetaminophen inside 48 hours after vaccination[⁴⁷]
• 11% obtain it prophylactically (earlier than vaccination)[⁴⁷]
• Acetaminophen used 2.6x extra ceaselessly than ibuprofen[⁴⁷]
• Oral analgesics utilized in 81% of practices throughout injection, 89% post-injection[⁴⁸]
WHY NEWBORNS ARE UNIQUELY VULNERABLE
**Lack of Maternal Safety:** At delivery, the new child loses maternal metabolic safety and should deal with acetaminophen utilizing its personal immature enzyme methods.[²⁴⁻²⁵⁻⁴⁹⁻⁵⁰]
Immature Cleansing Capability:[⁴⁹⁻⁵²]
• Glucuronidation severely underdeveloped (main grownup pathway barely capabilities in newborns)
• Sulfation predominates however simply saturated
• Restricted glutathione reserves (particularly in preterm/sick infants)
• Impaired NAPQI cleansing
When sulfation is saturated, extra acetaminophen is compelled via the oxidative pathway to NAPQI—when glutathione reserves are least in a position to deal with it.
THE COMPOUNDING EFFECT
**Earlier than Start:** Mom has compromised glutathione → takes acetaminophen → growing fetal mind uncovered to NAPQI → fetus can not successfully detoxify → impaired neurodevelopment and neuronal harm
**After Start:** Child loses maternal safety → immature cleansing methods → low glutathione → receives acetaminophen at 2, 4, 6, 12 months with vaccinations → every dose additional depletes restricted glutathione → cumulative burden might exceed threshold for wholesome neurodevelopment → neuronal harm and regression from beforehand achieved milestones might happen
THE MATH THAT CONNECTS PRENATAL AND POSTNATAL EXPOSURE
• 200,000+ pregnancies per 12 months contain acetaminophen use in ladies with compromised glutathione
• Of these 200,000 susceptible prenatal exposures, 64% of infants will obtain acetaminophen inside 48 hours of first vaccination
• That’s roughly 128,000 infants per 12 months with susceptible prenatal publicity AND postnatal acetaminophen
• 100,000 kids identified with neurodevelopmental issues yearly
Many obtain acetaminophen repeatedly—after vaccinations at 2, 4, 6, and 12-15 months. Every dose represents one other hit on an already compromised system.
This isn’t about vaccines inflicting neurodevelopmental issues. That is a few frequent treatment observe that will symbolize one publicity too many for infants already susceptible from prenatal exposures and maternal metabolic dysfunction.
THE BOTTOM LINE: IS TYLENOL SAFE FOR PREGNANCY?
The dramatic rise in neurodevelopmental dysfunction prevalence factors to environmental elements taking part in a major position. Acetaminophen use throughout being pregnant—and after delivery in infancy—seems to be one environmental issue amongst many that may work together with underlying vulnerabilities.
The important thing understanding: **Acetaminophen itself isn’t poisonous. It solely turns into poisonous when the physique can not correctly metabolize it via secure cleansing pathways and as a substitute converts it into the poisonous metabolite NAPQI.**
The proof suggests acetaminophen doesn’t trigger neurodevelopmental issues in infants born to ladies with sturdy cleansing methods. Nonetheless, in people with compromised glutathione standing, impaired cleansing pathways, poor methylation, genetic variants, or a number of environmental stressors, the physique generates extra NAPQI—the poisonous metabolite that crosses the placenta, depletes fetal mind glutathione, and damages growing neurons.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
1. **The fetus can not detoxify acetaminophen successfully** and depends totally on maternal metabolism. Fetal metabolism makes use of sulfation pathways that grow to be saturated, shunting extra drug to the poisonous NAPQI pathway.[²⁴⁻²⁵⁻¹⁰⁰]
2. **NAPQI is neurotoxic:** NAPQI crosses the placenta, depletes fetal mind glutathione, generates oxidative stress, damages mitochondria, and triggers cell dying in neural tissue at doses under these inflicting maternal liver toxicity. Youngsters with highest twine blood ranges of NAPQI-related metabolites face 2-3x greater odds of consideration/focus issues.[⁷³⁻⁷⁵⁻¹⁰⁰]
3. **Being pregnant INCREASES acetaminophen toxicity:** The Brookhuis 2021 examine demonstrates that being pregnant causes an 80% enhance within the poisonous CYP2E1 pathway that generates NAPQI, 43% greater NAPQI in first trimester when fetal mind is most susceptible, and 33% lower in secure sulfation pathway—whereas glutathione concurrently depletes by 36-87% all through being pregnant.[⁶⁰⁻¹⁰²⁻¹⁰⁴]
4. **Even ladies who really feel superb might have fetuses experiencing harm:** The pregnancy-induced shift towards oxidation (↑80%) mixed with decreased sulfation (↓33%) and depleted glutathione (↓36-87%) creates most vulnerability. A mom feeling properly doesn’t imply her fetus isn’t experiencing glutathione depletion and oxidative mind harm.[⁶⁰⁻¹⁰²]
5. **Deadly outcomes documented at therapeutic doses:** Gao et al. 2022 reported the primary deadly case—a pregnant girl with intrahepatic cholestasis died from liver failure after therapeutic acetaminophen doses. A number of liver transplant instances documented at supratherapeutic doses with fetal dying.[⁵⁸⁻¹⁰⁶]
6. **Dose-response relationship helps causation:** Clear dose-response patterns—longer acetaminophen use correlates with greater consideration/focus dysfunction threat, with strongest proof linking prenatal NAPQI publicity to consideration and behavioral issues.[⁷⁷⁻⁷⁹]
7. **A number of threat elements compound vulnerability:** Low sulfur amino acid consumption, blood sugar dysregulation, persistent infections, chemical exposures, genetic variants, IVF conception (70-83% depleted antioxidants), PCOS (50% decrease glutathione), gallbladder dysfunction (10%), and choline deficiency (89%) severely compromise glutathione standing and cleansing pathways.[¹⁷⁻¹⁹⁻³⁷⁻⁴⁶⁻⁶¹⁻⁶³]
8. **The numbers align:** 200,000+ susceptible pregnancies per 12 months involving acetaminophen publicity and 100,000 neurodevelopmental dysfunction instances yearly (plus a whole lot of hundreds of consideration/focus dysfunction instances).
9. **Postnatal publicity provides cumulative burden:** 64% of infants obtain acetaminophen after vaccination, and for these already susceptible from prenatal exposures, this will symbolize “the final straw” exceeding metabolic capability.[⁴⁷⁻⁴⁸]
WHAT SLOWS AND SPEEDS UP YOUR DETOX ENZYMES
Even for those who don’t have genetic variations in cleansing enzymes, your way of life, food regimen, medicines, and environmental exposures can considerably influence how effectively your physique processes acetaminophen.
GLUCURONIDATION (UGT1A6 Enzyme) – THE SAFE PATHWAY
What SLOWS UGT1A6 (Makes It “Soiled”):
Environmental Chemical substances:
• Persistent organochlorine pollution (PCBs, DDT, bisphenol A/BPA, dioxins)
• Xenobiotic compounds in cloth dyes, hair dyes, pores and skin lightening merchandise
• Sure pesticides and herbicides
• Polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from grilling, charring, barbecuing, deep-frying
• Produce grown close to highways or air pollution sources
Way of life Elements:
• Advancing age (naturally declines)
• Females have decrease expression than males
• Irritation and infections (particularly LPS from bacterial infections and leaky intestine)
• Power stress
Meals:
• Artificial meals dyes (halogenated xanthene meals dyes, phloxine, erythrosine, rose bengal)
• Excessive-temperature cooked meals (burnt toast, charred meats, deep-fried meals)
• Cured/smoked deli meats, bread from wood-fired ovens
Drugs:109
• NSAIDs (ibuprofen, naproxen)
• Aspirin
• Acetaminophen itself (when used repeatedly)
• Glimepiride (kind II diabetes treatment) is a powerful inhibitor of UGT1A6
• Tamazapan (Bebzodiazapine, sleeping treatment)
• Mefenamic acid (ache reduction for main dysmenorrhea)
• Ketoconazole (antifungal therapy for systemic fungal infections)
• Itraconazole (antifungal therapy for each systemic and superficial fungal infections)
• Verapamil (angina treatment)
• Ritonavir (antiretroviral brokers for HIV-1 an infection)
Herbs (worse when mixed with medicines):
• Milk thistle (Silybum marianum)
• Astragalus (Astragali radix)
• St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum)
• Noticed palmetto (Serenoa repens)
• Cranberry
• Excessive-coumarin herbs: wormwood, mullein, candy clover, dong quai, peppermint, spearmint
What SPEEDS UP UGT1A6 (Retains It “Clear”):
Meals:
• Cruciferous greens (broccoli, kale, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts)
• Onions and garlic (excessive in quercetin and sulfur compounds)
• Excessive-quality natural espresso (will increase glucuronidation)
• Inexperienced tea, rooibos tea, honeybush tea, dandelion tea
• Rosemary and lemon juice (particularly when roasting)
Cooking Strategies:
• Braising, stewing, slow-cooking (decrease, oblique warmth)
• Marinating meats 4+ hours earlier than grilling (reduces damaging polyaromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) formation)
Dietary supplements†:
• Calcium-D-glucarate
• Quercetin (paradoxically helps regardless of technical slowing)
• Curcumin
• Vitamin C, vitamin E (antioxidants assist a wholesome response to oxidative stress)
• Glutathione or N-acetylcysteine (NAC)
SULFATION (SULT Enzymes) – THE SAFE PATHWAY
What SLOWS Sulfation (Makes It “Soiled”):
Dietary Deficiencies:
• Low sulfur amino acid consumption (vegetarian/vegan diets with out sufficient protein)
• Insufficient protein consumption
• Low consumption of eggs, poultry, fish, cruciferous greens
Nutrient Depletions:
• Molybdenum deficiency (wanted for sulfite oxidase)
• Vitamin B6 deficiency
• Magnesium deficiency
Environmental Exposures:
• Sulfite-containing meals and preservatives (wines, dried fruits, processed meals)
• Excessive poisonous steel burden (depletes sulfur reserves)
Drugs:108
• Mefenamic acid (ache reduction for dysmenorrhea) strongly inhibits SULT1A1
• NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicine) akin to nimesulide, meclofenamate, piroxicam, aspirin, ibuprofen, and salicylic acid (aspirin)
• Clomiphene (used to induce ovulation in ladies needing being pregnant), together with these with polycystic ovary syndrome, amenorrhea-galactorrhea syndrome, psychogenic amenorrhea, and sure instances of secondary amenorrhea.
• Danazol (therapy for endometriosis)
• Spironolactone (coronary heart failure and hypertension treatment)
• Cyclizine and Dimenhydrinate (therapy for nausea, vomiting, movement illness, and vertigo).
• Chlorpheniramine (antihistamine, hay fever treatment)
Herbs (worse when mixed with medicines):110
• Quercetin and resveratrol (wine and pink berries)
• ECGC (present in inexperienced tea)
• Grape seed
• St. John’s wort (Hypericum perforatum)
• Milk thistle (Silybum marianum)
• Gingko biloba leaf
• Gymnema (kind 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome and weight administration)
• Banaba (medicinal leaf extracts). Antihyperglycemic used for diabetes and metabolic syndrome
• Astragalus (Astragali radix)
• Turmeric spice (curcumin)
• Fruit juces: grapefruit juice, orange juice
• Teas: inexperienced tea, black tea and oolong tea
Genetic Elements:
• SUOX gene gradual variants (sulfite oxidase deficiency)
• CBS gene gradual variants (can impair sulfur metabolism)
What SPEEDS UP Sulfation (Retains It “Clear”):
Meals:
• Excessive-sulfur meals: eggs, garlic, onions, cruciferous greens
• High quality animal protein: grass-fed beef, pasture-raised poultry, wild-caught fish
• Alliums: garlic, onions, leeks, shallots
• Brassicas: broccoli, cabbage, kale, Brussels sprouts, cauliflower
Dietary supplements†:
• MSM (methylsulfonylmethane)
• Taurine
• Alpha-lipoic acid
• Molybdenum
• Vitamin B6
• Magnesium
• N-acetylcysteine (NAC)
CYP2E1 ENZYME – THE TOXIC PATHWAY
What SPEEDS UP CYP2E1 (INCREASES Poisonous NAPQI Manufacturing):
That is the enzyme you need to SLOW DOWN throughout being pregnant as a result of it creates the poisonous NAPQI metabolite.
Way of life Elements:
• Power alcohol consumption (main inducer)
• Fasting or calorie restriction
• Excessive-fat ketogenic food regimen
• Weight problems (will increase CYP2E1 expression)
• Diabetes and insulin resistance
Drugs:
• Isoniazid (TB treatment)
• Some anticonvulsants
Environmental:
• Acetone publicity (nail polish remover, industrial solvents)
• Benzene publicity
What SLOWS DOWN CYP2E1 (DECREASES Poisonous NAPQI Manufacturing):
That is what you WANT throughout being pregnant to scale back poisonous metabolite formation.
Meals and Compounds:
• Watercress (potent CYP2E1 inhibitor)
• Garlic (diallyl sulfide inhibits CYP2E1)
• Inexperienced tea (EGCG)
• Curcumin (turmeric)
• Quercetin (onions, apples)
• Ellagic acid (pomegranate, berries)
• Fish oil (omega-3 fatty acids)
Way of life:
• Keep away from alcohol utterly
• Preserve secure blood sugar
• Satisfactory protein consumption (prevents enzyme induction from fasting)
• Keep away from ketogenic diets throughout being pregnant
THE STRATEGIC APPROACH FOR PREGNANT WOMEN
To reduce acetaminophen toxicity threat:
1. **Help Glucuronidation**: Eat cruciferous greens, drink inexperienced tea away from meals
2. **Help Sulfation**: Guarantee sufficient protein and sulfur-rich meals (eggs, garlic, onions, cruciferous greens)
3. **Gradual Down CYP2E1**: Embrace watercress, garlic, keep away from alcohol and fasting
4. **Maximize Glutathione**: Satisfactory protein, vitamin C, vitamin E, B nutritional vitamins, take into account NAC supplementation below healthcare steering†
TWO HIGH-RISK EXAMPLES
——————————————————————
**PCOS:** A girl with PCOS begins being pregnant with 50% decrease glutathione. She has 3-4x greater threat of preeclampsia or gestational blood sugar points—additional depleting glutathione. Her sulfation capability decreases 33% throughout being pregnant. She’s choline poor (89% of pregnant ladies), impairing liver operate. She develops gallbladder sludge (10% of pregnancies). Add a vegetarian food regimen low in sulfur amino acids, newly transformed residence with formaldehyde off-gassing, and repeated acetaminophen for complications—her cleansing system shunts extra acetaminophen to poisonous NAPQI formation. NAPQI crosses the placenta, depletes her child’s mind glutathione, and damages growing neurons. This isn’t about acetaminophen “inflicting” neurodevelopmental issues—it’s a few cascade of vulnerabilities reaching a tipping level.
**IVF:** A girl who conceived through IVF has 70-83% depleted antioxidant capability. Her oxidative stress markers elevated 50-100%+. Being pregnant will increase her poisonous NAPQI manufacturing 80% whereas depleting her already-low glutathione. She’s choline poor (89% chance). She develops intrahepatic cholestasis (0.4-10% of pregnancies), which has been related to deadly outcomes from therapeutic acetaminophen doses. Add PCOS (frequent in IVF), gestational diabetes, environmental exposures, food regimen not optimized for sulfur amino acids, and acetaminophen use—her impaired cleansing pathways produce poisonous NAPQI. NAPQI crosses into her child’s growing mind, depletes restricted fetal glutathione reserves, and damages neural cells. Then her toddler receives acetaminophen after vaccinations at 2, 4, 6, and 12 months. The toddler’s immature glucuronidation forces much more acetaminophen via the poisonous CYP2E1 pathway, creating NAPQI the toddler’s restricted glutathione can not neutralize, inflicting one other spherical of oxidative harm to the still-developing mind. This situation impacts a whole lot of hundreds of pregnancies yearly.
The objective isn’t to create concern round acetaminophen use, however to grasp that particular person metabolic context issues. Neurodevelopmental issues probably consequence from cumulative burden of a number of environmental hits on genetically or metabolically susceptible people. No single publicity “causes” these situations, however the mixture of compromised cleansing capability, poor dietary standing, chemical exposures, metabolic dysfunction, and extra stressors like acetaminophen throughout essential developmental home windows—each prenatal and postnatal—might push inclined people over the brink.
The hazard isn’t acetaminophen as a molecule—it’s the poisonous metabolite created when susceptible populations with impaired cleansing capability attempt to course of it.
SUPPORTIVE SUPPLEMENTS TO OPTIMIZE A HEALTHY PREGNANCY†
Whereas food regimen and way of life kind the inspiration of wholesome cleansing, focused supplementation can present extra assist—particularly for girls with recognized threat elements like PCOS, IVF conception, choline deficiency, or genetic variants affecting cleansing pathways.
**OPTIMAL PRENATAL – COMPREHENSIVE FOUNDATION**
A high-quality prenatal multivitamin addresses a number of pathways concurrently. In search of Well being’s Optimum Prenatal gives†:
>>> For Glutathione Help: <<<
• S-Acetyl Glutathione – A secure, bioavailable kind that crosses cell membranes successfully
• Vitamin C – Helps glutathione recycling and regeneration
• Vitamin E – Works synergistically with glutathione to assist a wholesome response to oxidative stress
• Selenium – Cofactor for glutathione peroxidase enzyme
For Methylation and Homocysteine Metabolism:
• Trimethylglycine (TMG/Betaine) – Helps methylation pathways and wholesome homocysteine metabolism
• Methylated B nutritional vitamins (B6, methylfolate, methylcobalamin) – Important for one-carbon metabolism
• Choline – Crucial for methylation, liver operate, and fetal mind growth (89% of pregnant ladies are poor)
For Mobile Vitality and Antioxidant Protection:
• CoQ10 (ubiquinone) – Helps mitochondrial operate and acts as a potent antioxidant
• Vitamin D – Helps immune operate and helps wholesome ranges of irritation
Why This Issues for Acetaminophen Metabolism:
The mix of glutathione assist, methylation cofactors, and choline addresses the core vulnerabilities that make acetaminophen poisonous in being pregnant. S-acetyl glutathione gives direct glutathione assist, whereas TMG and choline optimize the pathways that preserve glutathione ranges and assist wholesome liver operate.†
**OPTIMAL PC – TARGETED CHOLINE AND PHOSPHOLIPID SUPPORT**
With 89% of pregnant ladies poor in choline, and choline deficiency straight impairing liver operate and rising acetaminophen toxicity threat, extra phosphatidylcholine supplementation could also be useful.
In search of Well being’s Optimum PC gives†:
• Phosphatidylcholine – Probably the most bioavailable type of choline
• Helps PEMT enzyme operate (phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase)
• Important for liver well being, cell membrane integrity, and methylation
• Crucial for fetal mind growth
Why PEMT Enzyme Issues:
The PEMT enzyme produces phosphatidylcholine utilizing methylation pathways. Ladies with PEMT gene variants, these below metabolic stress (being pregnant, PCOS, IVF), or these with insufficient choline consumption can not produce ample phosphatidylcholine. This impairs:
• Liver cleansing capability (together with acetaminophen metabolism)
• Cell membrane operate and restore
• Lipid metabolism and bile manufacturing
• Fetal neurodevelopment
Who Advantages Most:
• Pregnant ladies not assembly choline necessities via food regimen (89% of girls)
• Ladies with PCOS, fatty liver, or metabolic syndrome
• Ladies who conceived through IVF (already depleted antioxidant standing)
• Vegetarians/vegans (plant-based diets sometimes very low in choline)
• Ladies with PEMT or MTHFR genetic variants
**GLUTATHIONE WITH COFACTORS LOZENGE – ADDITIONAL GLUTATHIONE SUPPORT**
For girls with recognized glutathione depletion (PCOS with 50% decrease glutathione, IVF with 70-83% depleted antioxidants, lively infections, excessive poisonous burden), extra light glutathione assist could also be useful.†
In search of Well being’s Glutathione with Cofactors Lozenge gives†:
• Diminished L-glutathione – The lively, bioavailable kind
• Supportive cofactors – Nutritional vitamins and minerals that assist glutathione operate
• Lozenge kind – Permits environment friendly and fast absorption
• Nice style – Makes compliance simpler
• Versatile dosing – May be divided into smaller items (halves or quarters) for kids or delicate people
• Light formulation – Nicely-tolerated, secure for younger kids
Why Lozenge Type:
Glutathione taken orally in capsule kind is basically damaged down within the digestive system. The lozenge permits for fast and effiecientabsorption, enhancing bioavailability whereas being light on the system.
Easy methods to Use:
• Adults: 1 full lozenge day by day, or as directed by healthcare supplier
• Youngsters: May be divided into 2-4 items relying on age and wish
• Greatest taken away from meals for optimum absorption
• Dissolves simply – may be chewed or allowed to dissolve slowly
Who Advantages Most:
• Ladies with PCOS (50% decrease baseline glutathione)
• Ladies who conceived through IVF (severely depleted antioxidant standing)
• Ladies with gestational blood sugar points or blood sugar dysregulation
• Ladies with persistent infections (EBV, CMV) or inflammatory situations
• Ladies with excessive environmental poisonous burden
• Ladies with GSTM1/GSTT1 genetic deletions (impaired glutathione conjugation)
• Postnatal use: Youngsters who acquired acetaminophen after vaccinations or prenatal publicity
**THE STRATEGIC SUPPLEMENT APPROACH**
Baseline for All Pregnant Ladies:
• Optimum Prenatal – Offers complete basis with glutathione, methylation assist, choline, and antioxidants†
For Choline Deficiency (89% of girls), add:
• Optimum PC – Ensures sufficient phosphatidylcholine for liver operate and PEMT enzyme assist†
For Excessive-Danger Situations, add:
• Glutathione with Cofactors Lozenge – Offers extra light glutathione assist for†:
– PCOS (50% decrease glutathione)
– IVF conception (70-83% depleted antioxidants)
– Gestational blood sugar points
– Wholesome immune response for persistent infections
– Response to excessive poisonous burden
– Genetic variants affecting glutathione pathways
Necessary Notes:
• All the time seek the advice of together with your healthcare supplier earlier than beginning any complement routine throughout being pregnant
• These dietary supplements assist wholesome cleansing pathways however don’t remove the necessity to reduce acetaminophen use when doable
• Work with a useful medication practitioner to evaluate your particular person threat elements and optimize your supplementation technique
• High quality issues – select dietary supplements from respected producers that endure third-party testing
• Keep in mind that dietary supplements work finest as a part of a complete strategy together with nutrient-dense food regimen, sufficient protein, sulfur-rich meals, and minimized environmental exposures
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS ABOUT TYLENOL AND PREGNANCY
**1. IS TYLENOL SAFE FOR PREGNANCY?**
Tylenol (acetaminophen) security throughout being pregnant is determined by particular person metabolic context. For girls with sturdy glutathione ranges and wholesome cleansing pathways, occasional use at really useful doses seems to pose minimal threat.[¹⁻⁵] Nonetheless, for girls with compromised glutathione standing (PCOS[¹⁷⁻³⁷⁻⁴⁰], IVF conception[¹⁸⁻¹⁹⁻⁴¹⁻⁴⁶], gestational blood sugar points, poor food regimen, environmental exposures), even therapeutic doses might generate poisonous metabolites that cross the placenta and have an effect on fetal mind growth.[²⁴⁻²⁵⁻⁶⁰⁻⁷³⁻⁷⁵⁻¹⁰⁰] The hot button is understanding your particular person threat elements slightly than following blanket suggestions.
**2. HOW MUCH TYLENOL CAN I TAKE WHILE PREGNANT?**
The usual advice is 500-650 mg each 4-6 hours as wanted, not exceeding 4,000 mg per day.[¹⁵⁻¹⁶⁻²⁰] Nonetheless, this “secure” dose assumes regular cleansing capability. Throughout being pregnant, your physique produces 80% MORE of the poisonous NAPQI metabolite (43% greater in first trimester), sulfation capability decreases 33%, and glutathione depletes 36-87% all through being pregnant.[⁶⁰⁻¹⁰²⁻¹⁰⁴] You probably have extra threat elements (PCOS with 50% decrease glutathione[¹⁷⁻³⁷⁻⁴⁰], IVF with 70-83% depleted antioxidants[¹⁸⁻¹⁹⁻⁴¹⁻⁴⁶], gallbladder points[⁵³⁻⁶⁰], choline deficiency affecting 89% of pregnant ladies[⁶¹⁻⁶³]), your efficient “secure” dose could also be considerably decrease—and even therapeutic doses could also be harmful. Deadly liver failure has been documented at therapeutic doses in pregnant ladies with intrahepatic cholestasis.[⁵⁸] Contemplate discussing your particular person threat elements together with your healthcare supplier to find out applicable dosing on your particular state of affairs.
**3. DOES TYLENOL CAUSE NEURODEVELOPMENTAL DISORDERS?**
Tylenol doesn’t straight trigger neurodevelopmental issues. Moderately, the poisonous metabolite NAPQI—created when your physique can not correctly course of acetaminophen via secure pathways—depletes glutathione and generates oxidative stress within the growing mind.[⁷³⁻⁷⁵⁻¹⁰⁰] Analysis exhibits clear dose-response relationships: kids with highest twine blood ranges of NAPQI-related metabolites face 2-3x greater odds of consideration/focus issues and elevated neurodevelopmental issues.[¹¹⁻¹⁴⁻⁷⁷⁻⁷⁹] The 200,000+ annual pregnancies involving acetaminophen use in ladies with compromised glutathione[¹⁷⁻¹⁹⁻³⁷⁻⁴⁶⁻⁶⁰⁻⁶³⁻¹⁰²⁻¹⁰⁴] suggests acetaminophen could also be one environmental issue that interacts with underlying vulnerabilities in inclined people.
**4. WHAT ARE THE RISK FACTORS THAT MAKE TYLENOL MORE DANGEROUS DURING PREGNANCY?**
Main threat elements embody:
• PCOS (50% decrease glutathione ranges)[¹⁷⁻³⁷⁻⁴⁰]
• IVF conception (70-83% depleted antioxidant capability)[¹⁸⁻¹⁹⁻⁴¹⁻⁴⁶]
• Gestational diabetes or blood sugar dysregulation
• Gallbladder dysfunction (impacts 10% of pregnancies)[⁵³⁻⁶⁰]
• Choline deficiency (impacts 89% of pregnant ladies)[⁶¹⁻⁶³]
• Low sulfur amino acid consumption (vegetarian/vegan diets with out sufficient protein)
• Environmental exposures (chlorine, formaldehyde, VOCs, pesticides)
• Genetic variants affecting cleansing (CBS, CYP2E1, MTHFR, GSTM1/GSTT1)
• Power infections, liver situations, weight problems, metabolic syndrome
**5. SHOULD I GIVE MY BABY TYLENOL AFTER VACCINATIONS?**
It is a advanced query requiring individualized consideration. Whereas 64% of infants obtain acetaminophen after vaccination,[⁴⁷⁻⁴⁸] newborns have severely underdeveloped cleansing methods.[⁴⁹⁻⁵²] Their main grownup pathway (glucuronidation) barely capabilities, forcing extra acetaminophen via the poisonous oxidation pathway to NAPQI.[²⁴⁻²⁵⁻⁶⁰] In case your child was uncovered to prenatal acetaminophen throughout a susceptible being pregnant (PCOS, IVF, metabolic points), post-vaccination doses might symbolize cumulative burden exceeding their restricted glutathione capability. Talk about together with your pediatrician whether or not acetaminophen is important, take into account alternate options like ibuprofen (after 6 months), and weigh your child’s particular person threat profile.
**6. WHAT CAN I DO TO SUPPORT HEALTHY DETOXIFICATION DURING PREGNANCY?**
To optimize acetaminophen metabolism and reduce toxicity threat:
Help Glucuronidation (Protected Pathway):
• Eat cruciferous greens day by day (broccoli, kale, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts)
• Drink high-quality inexperienced tea, rooibos tea, dandelion tea
• Embrace garlic and onions
• Contemplate calcium-D-glucarate supplementation†
• Keep away from artificial meals dyes and high-temperature cooking (grilling, charring)
Help Sulfation (Protected Pathway):
• Guarantee sufficient high-quality protein (eggs, poultry, fish)
• Eat sulfur-rich meals: garlic, onions, cruciferous greens
• Contemplate MSM, taurine, or alpha-lipoic acid supplementation†
• Guarantee sufficient vitamin B6, magnesium, molybdenum
Gradual Down CYP2E1 (Poisonous Pathway):
• Embrace watercress recurrently (potent CYP2E1 inhibitor)
• Eat garlic day by day (diallyl sulfide inhibits CYP2E1)
• Drink inexperienced tea (EGCG) away from meals
• Use turmeric/curcumin
• Keep away from alcohol utterly
• Preserve secure blood sugar (keep away from fasting)
>>> Maximize Glutathione: <<<
• Satisfactory protein consumption with sulfur amino acids
• Guarantee choline necessities (eggs, liver, fish, cruciferous greens)
• Complement with nutritional vitamins C and E†
• Guarantee sufficient B nutritional vitamins (B6, B12, folate) for methylation assist†
• Reduce environmental exposures (chlorinated water, VOCs, formaldehyde)
• Contemplate N-acetylcysteine (NAC) supplementation below healthcare supplier steering†
• Work with a useful medication practitioner to optimize metabolic well being earlier than and through being pregnant
IMPORTANT MEDICAL DISCLAIMER
This text is for academic functions solely and isn’t meant as medical recommendation. All the time seek the advice of together with your healthcare supplier relating to treatment use throughout being pregnant and any issues about your particular person threat elements.

Dr. Ben Lynch is the best-selling writer of Soiled Genes® and President of In search of Well being, an organization that helps educate each the general public and well being professionals on the right way to overcome genetic dysfunction. He acquired his doctorate in naturopathic medication from Bastyr College. He lives in Seattle, WA along with his spouse and three sons. www.drbenlynch.com
COMPLETE REFERENCES
1. D’Souza SW, Glazier JD. Homocysteine Metabolism in Being pregnant and Developmental Impacts. Entrance Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:802285.
2. García-Giménez JL, Romá-Mateo C, Pérez-Machado G, Peiró-Chova L, Pallardó FV. Position of Glutathione within the Regulation of Epigenetic Mechanisms in Illness. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017;112:36-48.
3. Akhtar F, Rouse CA, Catano G, et al. Acute Maternal Oxidant Publicity Causes Susceptibility of the Fetal Mind to Irritation and Oxidative Stress. J Neuroinflammation. 2017;14(1):195.
4. Kalhan SC. One Carbon Metabolism in Being pregnant: Affect on Maternal, Fetal and Neonatal Well being. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2016;435:48-60.
5. Liu J, Chu M, Zhang J, et al. Glutathione Safeguards TET-dependent DNA Demethylation and Is Crucial for the Acquisition of Totipotency and Pluripotency Throughout Preimplantation Growth. FASEB J. 2024;38(3):e23453.
6. Morris G, Anderson G, Dean O, et al. The Glutathione System: A New Drug Goal in Neuroimmune Problems. Mol Neurobiol. 2014;50(3):1059-84.
7. Wu G, Fang YZ, Yang S, Lupton JR, Turner ND. Glutathione Metabolism and Its Implications for Well being. J Nutr. 2004;134(3):489-92.
8. D’Souza SW, Glazier JD. Homocysteine Metabolism in Being pregnant and Developmental Impacts. Entrance Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:802285.
9. Mistry HD, Williams PJ. The Significance of Antioxidant Micronutrients in Being pregnant. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2011;2011:841749.
10. Knapen MF, Mulder TP, Van Rooij IA, Peters WH, Steegers EA. Low Complete Blood Glutathione Ranges in Pregnancies Sophisticated by Preeclampsia or the Hemolysis, Elevated Liver Enzymes, Low Platelets Syndrome. Obstet Gynecol. 1998;92(6):1012-5.
11. Jiang HY, et al. Prenatal and postnatal publicity to acetaminophen in relation to autism spectrum and attention-deficit and hyperactivity signs in childhood: Meta-analysis in six European population-based cohorts. Eur Baby Adolesc Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34046850
12. Ji Y, Azuine RE, Zhang Y, et al. Affiliation of Wire Plasma Biomarkers of In Utero Acetaminophen Publicity With Danger of Consideration-Deficit/Hyperactivity Dysfunction and Autism Spectrum Dysfunction in Childhood. JAMA Psychiatry. 2020;77(2):180-189.
13. Bauer AZ, Kriebel D, Herbert MR, Bornehag CG, Swan SH. Prenatal Publicity to Acetaminophen and Danger for Consideration Deficit Hyperactivity Dysfunction and Autistic Spectrum Dysfunction: A Systematic Evaluate, Meta-Evaluation, and Meta-Regression Evaluation of Cohort Research. Int J Environ Res Public Well being. 2018. PMID: 29688261
14. Liew Z, et al. Analysis of the proof on acetaminophen use and neurodevelopmental issues utilizing the Navigation Information methodology. 2025. PMID: 40804730
15. Servey J, Chang J. Over-the-Counter Drugs in Being pregnant. Am Fam Doctor. 2014;90(8):548-55.
16. Bandoli G, Palmsten Okay, Chambers C. Acetaminophen Use in Being pregnant: Analyzing Prevalence, Timing, and Indication of Use in a Potential Start Cohort. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2020;34(3):237-246.
17. Bahri Khomami M, Shorakae S, Hashemi S, et al. Systematic Evaluate and Meta-Evaluation of Being pregnant Outcomes in Ladies With Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):5591.
18. Luke B. Being pregnant and Start Outcomes in {Couples} With infertility With and With out assisted Reproductive Expertise: With an Emphasis On US Inhabitants-Based mostly Research. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2017;217(3):270-281.
19. Bentov Y, Schenker J. IVF and Being pregnant Outcomes: The Triumphs, Challenges, and Unanswered Questions. J Ovarian Res. 2025;18(1):228.
20. TYLENOL Common Energy. FDA Drug Label. Meals and Drug Administration. Up to date 2024-11-07.
21. Pickering G, Macian N, Papet I, et al. N-Acetylcysteine Prevents Glutathione Lower and Does Not Intrude With Paracetamol Antinociceptive Impact at Therapeutic Dosage: A Randomized Double-Blind Managed Trial in Wholesome Topics. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2019;33(3):303-311.
22. Lauterburg BH. Analgesics and Glutathione. Am J Ther. 2002;9(3):225-33.
23. Emmett M. Acetaminophen Toxicity and 5-Oxoproline (Pyroglutamic Acid): A Story of Two Cycles, One an ATP-depleting Futile Cycle and the Different a Helpful Cycle. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014;9(1):191-200.
24. Conings S, Tseke F, Van den Broeck A, et al. Transplacental Transport of Paracetamol and Its Section II Metabolites Utilizing the Ex Vivo Placenta Perfusion Mannequin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019;370:14-23.
25. Mian P, Allegaert Okay, Conings S, et al. Integration of Placental Switch in a Fetal-Maternal Physiologically Based mostly Pharmacokinetic Mannequin to Characterize Acetaminophen Publicity and Metabolic Clearance within the Fetus. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2020;59(7):911-925.
26. McGill MR, Jaeschke H. Metabolism and Disposition of Acetaminophen: Latest Advances in Relation to Hepatotoxicity and Analysis. Pharm Res. 2013;30(9):2174-87.
27. Riches Z, Bloomer J, Patel A, Nolan A, Coughtrie M. Evaluation of Cryopreserved Human Hepatocytes as a Mannequin System to Examine Sulfation and Glucuronidation. Xenobiotica. 2009;39(5):374-81.
28-36. [Additional oxidative stress and pregnancy references – available in full bibliography]
37. Murri M, Luque-Ramírez M, Insenser M, Ojeda-Ojeda M, Escobar-Morreale HF. Circulating Markers of Oxidative Stress and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): A Systematic Evaluate and Meta-Evaluation. Hum Reprod Replace. 2013;19(3):268-88.
38. Chełchowska M, Jurczewska J, Gajewska J, et al. Antioxidant Protection Expressed as Glutathione Standing and Keap1-Nrf2 System Motion in Relation to Anthropometric Parameters and Physique Composition in Younger Ladies With Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023;12(3):730.
39. Abudawood M, Tabassum H, Alanazi AH, et al. Antioxidant Standing in Relation to Heavy Metals Induced Oxidative Stress in Sufferers With Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS). Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):22935.
40. Palomba S, de Wilde MA, Falbo A, et al. Being pregnant Issues in Ladies With Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Hum Reprod Replace. 2015;21(5):575-92.
41. Becatti M, Fucci R, Mannucci A, et al. A Biochemical Strategy to Detect Oxidative Stress in Infertile Ladies Present process Assisted Reproductive Expertise Procedures. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(2):E592.
42. Aurrekoetxea I, Ruiz-Sanz JI, Del Agua AR, et al. Serum Oxidizability and Antioxidant Standing in Sufferers Present process in Vitro Fertilization. Fertil Steril. 2010;94(4):1279-1286.
43. Palini S, Benedetti S, Tagliamonte MC, et al. Affect of Ovarian Stimulation for IVF/ICSI on the Antioxidant Defence System and Relationship to Final result. Reprod Biomed On-line. 2014;29(1):65-71.
44. Skalny AV, Tinkov AA, Voronina I, et al. Hair Hint Aspect and Electrolyte Content material in Ladies With Pure and in Vitro Fertilization-Induced Being pregnant. Biol Hint Elem Res. 2018;181(1):1-9.
45. Meijide S, Hernández ML, Navarro R, et al. Glutathione S-Transferase Exercise in Follicular Fluid From Ladies Present process Ovarian Stimulation: Position in Maturation. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014;75 Suppl 1:S41.
46. Ozkaya MO, Nazıroğlu M. Multivitamin and Mineral Supplementation Modulates Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Vitamin Ranges in Serum and Follicular Fluid of Ladies Present process in Vitro Fertilization. Fertil Steril. 2010;94(6):2465-6.
47. Saleh E, Swamy GK, Moody MA, Walter EB. Parental Strategy to the Prevention and Administration of Fever and Ache Following Childhood Immunizations: A Survey Research. Medical Pediatrics. 2017;56(5):435-442.
48. Taddio A, Manley J, Potash L, et al. Routine Immunization Practices: Use of Topical Anesthetics and Oral Analgesics. Pediatrics. 2007;120(3):e637-43.
49. Piñeiro-Carrero VM, Piñeiro EO. Liver. Pediatrics. 2004;113(4 Suppl):1097-106.
50. Allegaert Okay, van den Anker JN. Perinatal and Neonatal Use of Paracetamol for Ache Aid. Seminars in Fetal & Neonatal Medication. 2017;22(5):308-313.
51. Locci C, Cuzzolin L, Capobianco G, Antonucci R. Paracetamol Overdose within the New child and Toddler: A Life-Threatening Occasion. European Journal of Medical Pharmacology. 2021;77(6):809-815.
52. Isbister GK, Bucens IK, Whyte IM. Paracetamol Overdose in a Preterm Neonate. Archives of Illness in Childhood. Fetal and Neonatal Version. 2001;85(1):F70-2.
53. Sarkar M, Brady CW, Fleckenstein J, et al. Reproductive Well being and Liver Illness: Apply Steering by the American Affiliation for the Research of Liver Ailments. Hepatology. 2021;73(1):318-365.
54. Rahim MN, Williamson C, Kametas NA, Heneghan MA. Being pregnant and the Liver. Lancet. 2025;405(10477):498-513.
55. Lee RH, Mara Greenberg, Metz TD, Pettker CM. Society for Maternal-Fetal Medication Seek the advice of Collection #53: Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Being pregnant: Replaces Seek the advice of #13, April 2011. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;224(2):B2-B9.
56. Reau N, Munoz SJ, Schiano T. Liver Illness Throughout Being pregnant. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022;117(10S):44-52.
57. Tran TT, Ahn J, Reau NS. ACG Medical Guideline: Liver Illness and Being pregnant. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016;111(2):176-94.
58. Gao Y, Zhang R, Liang H, Huang Y. Hepatic Failure With Deadly Final result Throughout Being pregnant Following Administration of a Single Therapeutic Dose of Acetominophen: Case Report and Literature Evaluate. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2022;60(11):486-491.
59. Kamath P, Kamath A, Ullal SD. Liver Damage Related With Drug Consumption Throughout Being pregnant. World J Hepatol. 2021;13(7):747-762.
60. Brookhuis SAM, Allegaert Okay, Hanff LM, Lub-de Hooge MN, Dallmann A, Mian P. Modelling Instruments to Characterize Acetaminophen Pharmacokinetics within the Pregnant Inhabitants. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(8):1302.
61. Derbyshire EJ. Choline in Being pregnant and Lactation: Important Information for Medical Apply. Vitamins. 2025;17(9):1558.
62. Obeid R, Schön C, Derbyshire E, et al. A Narrative Evaluate on Maternal Choline Consumption and Liver Perform of the Fetus and the Toddler; Implications for Analysis, Coverage, and Apply. Vitamins. 2024;16(2):260.
63. Roeren M, Kordowski A, Sina C, Smollich M. Insufficient Choline Consumption in Pregnant Ladies in Germany. Vitamins. 2022;14(22):4862.
64-72. [Additional acetaminophen metabolism and toxicity references – available in full bibliography]
73. McGill MR, Jaeschke H. Metabolism and Disposition of Acetaminophen: Latest Advances in Relation to Hepatotoxicity and Analysis. Pharm Res. 2013;30(9):2174-87.
74. Chowdhury A, Nabila J, Adelusi Temitope I, Wang S. Present Etiological Comprehension and Therapeutic Targets of Acetaminophen-Induced Hepatotoxicity. Pharmacol Res. 2020;161:105102.
75. Blecharz-Klin Okay, Piechal A, Joniec-Maciejak I, Pyrzanowska J, Widy-Tyszkiewicz E. Paracetamol – Impact of Early Publicity on Neurotransmission, Spatial Reminiscence and Motor Efficiency in Rats. Behav Mind Res. 2014;268:257-64.
76. Viberg H, Eriksson P, Gordh T, Fredriksson A. Paracetamol (Acetaminophen) Administration Throughout Neonatal Mind Growth Impacts Cognitive Perform and Alters Its Analgesic and Anxiolytic Response in Grownup Male Mice. Toxicol Sci. 2014;138(1):139-47.
77. Jiang HY, et al. Prenatal and postnatal publicity to acetaminophen in relation to autism spectrum and attention-deficit and hyperactivity signs in childhood: Meta-analysis in six European population-based cohorts. Eur Baby Adolesc Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34046850
78. Bauer AZ, Kriebel D, Herbert MR, Bornehag CG, Swan SH. Prenatal Publicity to Acetaminophen and Danger for Consideration Deficit Hyperactivity Dysfunction and Autistic Spectrum Dysfunction: A Systematic Evaluate, Meta-Evaluation, and Meta-Regression Evaluation of Cohort Research. Int J Environ Res Public Well being. 2018. PMID: 29688261
79. Ji Y, Azuine RE, Zhang Y, et al. Affiliation of Wire Plasma Biomarkers of In Utero Acetaminophen Publicity With Danger of Consideration-Deficit/Hyperactivity Dysfunction and Autism Spectrum Dysfunction in Childhood. JAMA Psychiatry. 2020;77(2):180-189.
80. Liew Z, et al. Analysis of the proof on acetaminophen use and neurodevelopmental issues utilizing the Navigation Information methodology. 2025. PMID: 40804730
81. Ahlqvist VH, Sjöqvist H, Dalman C, et al. Acetaminophen Use Throughout Being pregnant and Youngsters’s Danger of Autism, ADHD, and Mental Incapacity. JAMA. 2024;331(14):1205-1214.
82. Avella-Garcia CB, Julvez J, Fortuny J, et al. Acetaminophen Use in Being pregnant and Neurodevelopment: Consideration Perform and Autism Spectrum Signs. Int J Epidemiol. 2016;45(6):1987-1996.
83-99. [Timeline and prevalence references available in full document]
100. Mian P, Allegaert Okay, Conings S, et al. Integration of Placental Switch in a Fetal-Maternal Physiologically Based mostly Pharmacokinetic Mannequin to Characterize Acetaminophen Publicity and Metabolic Clearance within the Fetus. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2020;59(7):911-925.
101. Paracetamol Glucuronide – an summary. ScienceDirect Subjects. [States: “In near-term pregnancy, the clearance of acetaminophen is increased by 50%, with clearance to acetaminophen glucuronide increasing by 140%, and clearance to oxidative metabolites of acetaminophen increasing by 80%.”]
102. Research of glutathione, glutathione reductase, glutathione peroxidase as antioxidant system throughout being pregnant. Frontiers in Well being Informatics. 2024;13.
103. Estimation of Glutathione Stage in Second Trimester of Being pregnant. Saudi Journal of Biomedical Analysis. 2019.
104. Kharb S. Low Complete Blood Glutathione Ranges in Pregnancies Sophisticated by Preeclampsia and Diabetes. Clin Chim Acta. 2000;294(1-2):179-83.
105. Knapen MF, Mulder TP, Van Rooij IA, Peters WH, Steegers EA. Low Complete Blood Glutathione Ranges in Pregnancies Sophisticated by Preeclampsia or the Hemolysis, Elevated Liver Enzymes, Low Platelets Syndrome. Obstet Gynecol. 1998;92(6):1012-5.
106. Thornton SL, Minns AB. Unintentional Power Acetaminophen Poisoning Throughout Being pregnant Leading to Liver Transplantation. J Med Toxicol. 2012;8(2):176-8.
107. Further liver transplant case (2013) – documented in medical literature on acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity throughout being pregnant.
108. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15487807/ and https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33915121/ and https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17073578/ https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30423313/ and https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1397064/
109. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22957438/ and https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40543327/ and https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22357286/
110. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26805467/ and https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12745871/ and https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17876860/